Hot in Journal CHEST: July 2020
By: Divya C. Patel (@divyacpateldo)
July 2, 2020
 Each month, we ask our Social Media Co-Editors of CHEST, to weigh in on the hot topics in CHEST. It's July, so let's hear from co-editor, Dr. Patel, as she outlines her highlights. After reviewing the issue, be sure to share your hot list on our Facebook, tweet with the hashtag #journalCHEST, or discuss in the CHEST LinkedIn group.
Each month, we ask our Social Media Co-Editors of CHEST, to weigh in on the hot topics in CHEST. It's July, so let's hear from co-editor, Dr. Patel, as she outlines her highlights. After reviewing the issue, be sure to share your hot list on our Facebook, tweet with the hashtag #journalCHEST, or discuss in the CHEST LinkedIn group.
I love summer and usually look forward to the long days and extended vacations. However, this year, like most people, my mind is on the COVID-19 pandemic. Coronavirus 2019 cases are increasing dramatically in the United States, which will lead to increased hospitalizations and death in the coming weeks. This month, I am highlighting a study from China about risk factors for mortality, Fleischner Society guidelines on the role of chest imaging during the pandemic, and an article that reminds us that although we prescribe treatment with good intentions the actual outcome can be influenced by patient behavior.
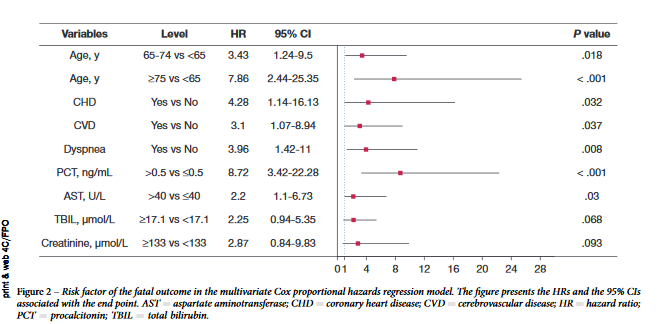
In this retrospective study, data from 1,590 hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection were analyzed to identify prognostic effects. A nomogram was developed to predict survival. Out of the cohort, 50 patients died and multivariate regression analysis showed age ≥75 years, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, presence of dyspnea, elevated procalcitonin, and elevated aspartate aminotransferase were associated with fatal outcome. Advanced age was the strongest risk factor for mortality.
Since obtaining chest imaging in patients with SARS-CoV-2 is complicated by the need to minimize transmission, a multidisciplinary panel consisting of radiologists and pulmonologists from 10 countries assessed 14 questions within clinical scenarios and related decision points. From this, five main and three additional recommendations regarding the use of chest radiography in COVID-19 patients were developed.
The panel highlight that chest imaging is not indicated in patients with suspected coronavirus 2019 infection unless at risk for progression or with worsening respiratory status. In resource-constrained situations, chest imaging can be used to triage patients with moderate-to-severe features.
This article provides three useful algorithms with various clinical presentations (including resource constraint setting), which can aid the clinician in deciding where imaging is indicated.
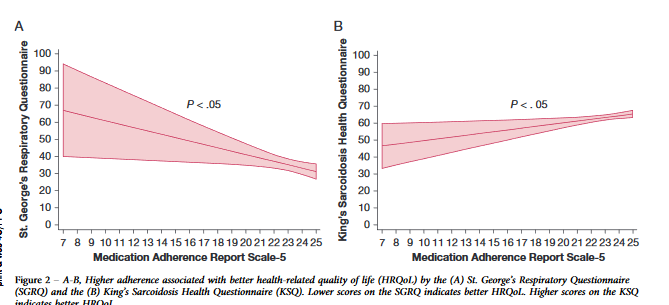
Nonadherence to treatment is an issue in many chronic conditions. Since the mainstay of treatment for sarcoidosis is prednisone and it is associated with many adverse effects, nonadherence may affect clinical outcomes. In this study, Sharp and colleagues administered questionnaires to 117 patients that assessed adherence, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and health-care utilization. The large majority of patients reported nonadherent behavior and showed association of higher adherence to better HRQoL. No association was found between medication adherence to lung function parameters.
Interestingly, in an accompanied editorial, Marc Judson outlines reasons for nonadherence and posits that poor communication between the patient and clinician is likely the most common cause for nonadherence. He also argues that poor HRQoL itself may be the driver of the nonadherent behavior.